
| Target Namespace | http://www.openmicroscopy.org/Schemas/SPW/2008-09 |
|---|---|
| Version | 1 |
| Element and Attribute Namespaces |
|
| Schema Composition |
|
| Documentation | Open Microscopy Environment Screen, Plate, and Well XML Schema Author: Andrew J Patterson |
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| Default namespace | http://www.openmicroscopy.org/Schemas/SPW/2008-09 |
| xml | http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace |
| xsd | http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema |
| OME | http://www.openmicroscopy.org/Schemas/OME/2008-09 |
| Name | ImageRef |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element WellSample |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | The ImageRef element is a reference to a OME:Image element. Note: at present this is only used from SPW. If it is used more widely in the future it will be moved into the main OME schema. |

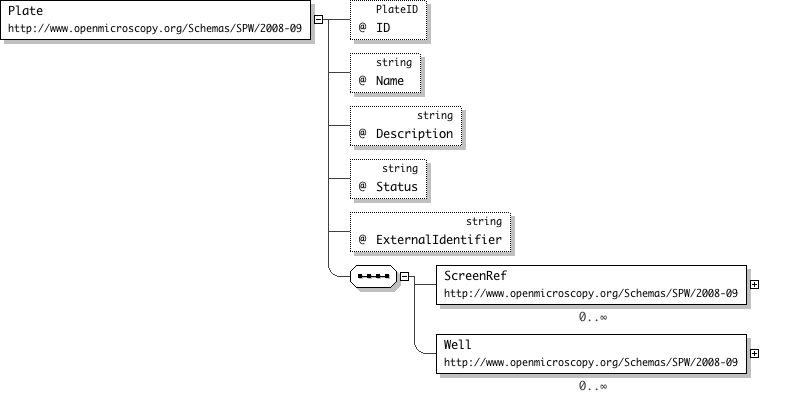
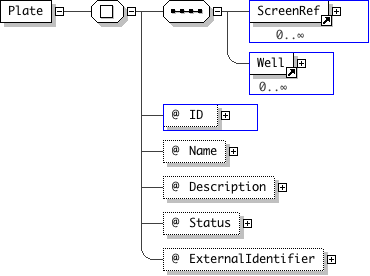
| Name | Plate |
|---|---|
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | This element identifies microtiter plates within a screen. A plate can belong to more than one screen. The Screen(s) that a plate belongs to are specified by the ScreenRef element. The Plate ID and Name attributes are required. The Wells in a plate are numbers from the top-left corner in a grid starting at zero. i.e The top-left well of a plate is index (0,0) |
'The Name identifies the plate to the user. It is used much like the ID, and so must be unique within the document.'
"'A textual annotation of the current state of the plate with respect to the experiment work-flow; e.g. 1. Seed cell: done; 2. Transfection: done; 3. Gel doc: todo.'
"'The ExternalIdentifier attribute may contain a reference to an external database.'
">
| Name | PlateRef |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Screen |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | The PlateRef element is a reference to a Plate element. Screen elements may have one or more PlateRef elements to define the plates that are part of the screen. Plates may belong to more than one screen. |

| Name | Reagent |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Screen |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
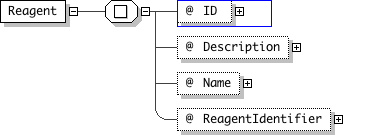
| Documentation | Reagent is used to describe a chemical or some other physical experimental parameter. |
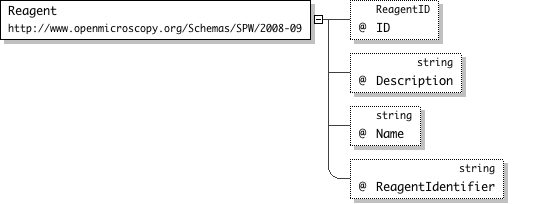
'A long description for the reagent'
"'A short name for the reagent'
"'This is a reference to an external (to OME) representation of the Reagent. It serves as a foreign key into an external database. - It is sometimes refereed to as ExternalIdentifier.'
"/>
| Name | ReagentRef |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Well |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |


| Name | Screen |
|---|---|
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
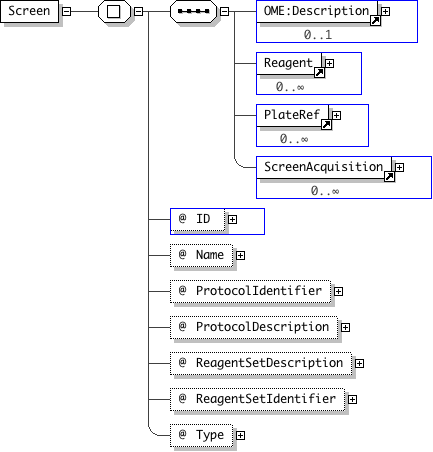
| Documentation | The Screen element is a grouping for Plates. The required attribute is the Screen's Name and ID - both must be unique within the document. The Screen element may contain an ExternalRef attribute that refers to an external database. A description of the screen may be specified in the Description element. Screens may contain overlapping sets of Plates i.e. Screens and Plates have a many-to-many relationship. Plates contain one or more ScreenRef elements to specify what screens they belong to. |
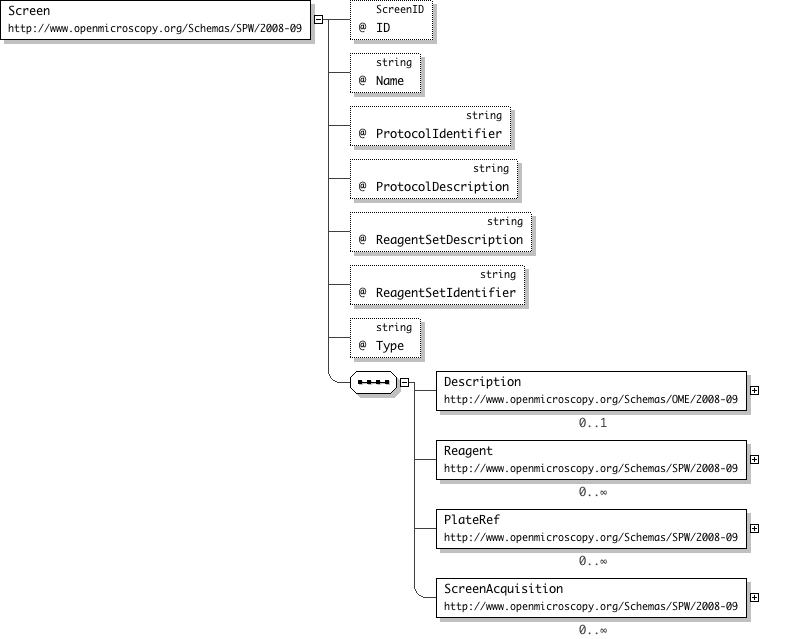
'A pointer to an externally defined protocol, usually in a screening database.'
"'A description of the screen protocol; may contain very detailed information to reproduce some of that found in a screening database.'
"'A description of the set of reagents; may contain very detailed information to reproduce some of that information found in a screening database.'
"'A pointer to an externally defined set of reagents, usually in a screening database/automation database.'
"'A human readable identifier for the screen type; e.g. RNAi, cDNA, SiRNA, etc. This string is likely to become an enumeration in future releases.'
">
| Name | ScreenAcquisition |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Screen |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | ScreenAcquisition is used to describe a single acquisition run for a screen. Since Screens are abstract, this object is used to record the set of images acquired in a single acquisition run. The Images for this run are linked to ScreenAcquisition through WellSample. |
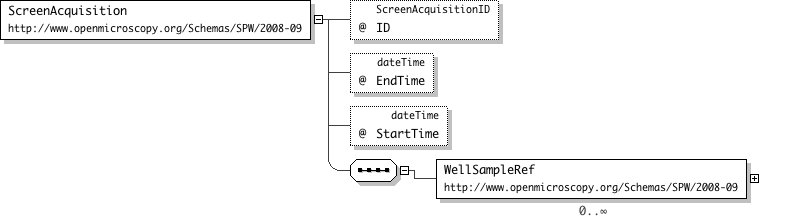
'Time when the last image of this acquisition was collected'
"'Time when the first image of this acquisition was collected'
">
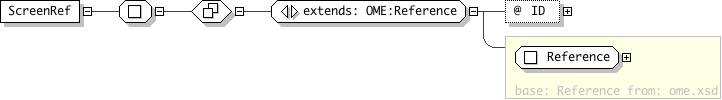
| Name | ScreenRef |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Plate |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | The ScreenRef element is a reference to a Screen element. Plate elements may have one or more ScreenRef elements to define the screen that a plate belongs to. Plates may belong to more than one screen. |

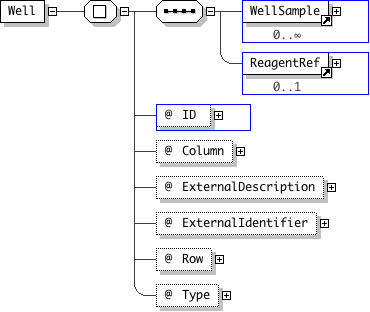
| Name | Well |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Plate |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | A Well is a component of the Well/Plate/Screen construct to describe screening applications. A Well has a number of WellSample elements that link to the Images collected in this well. The ReagentRef links any Reagents that were used in this Well. A well is part of only one Plate. The origin for the row and column identifiers is the top left corner of the plate starting at zero. i.e The top left well of a plate is index (0,0) |
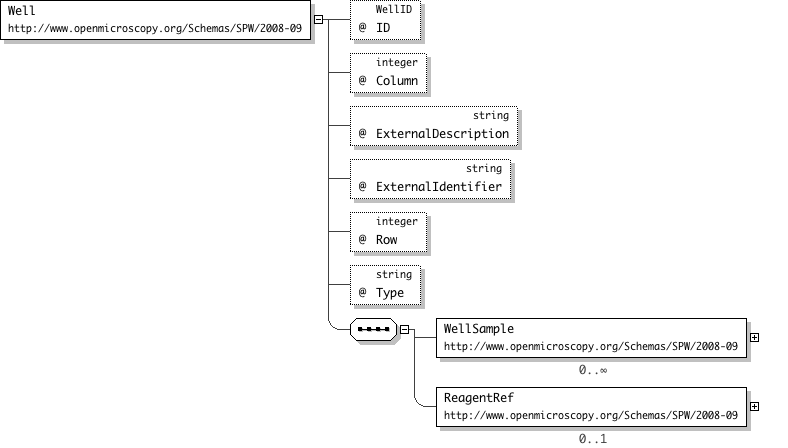
'This is the column index of the well, the origin is the top left corner of the plate with the first column of cells being column zero. i.e top left is (0,0)'
"'A description of the externally defined identifier for this plate.'
"'The ExternalIdentifier attribute may contain a reference to an external database.'
"'This is the row index of the well, the origin is the top left corner of the plate with the first row of wells being row zero. i.e top left is (0,0)'
"'A human readable identifier for the screening status. e.g. empty, positive control, negative control, control, experimental, etc. This string is likely to become an enumeration in future releases.'
">
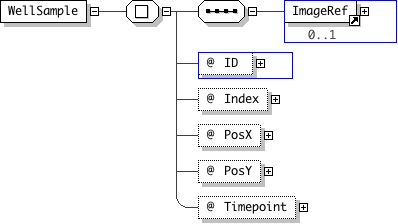
| Name | WellSample |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Well |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | WellSample is an individual image that has been captured within a Well. |
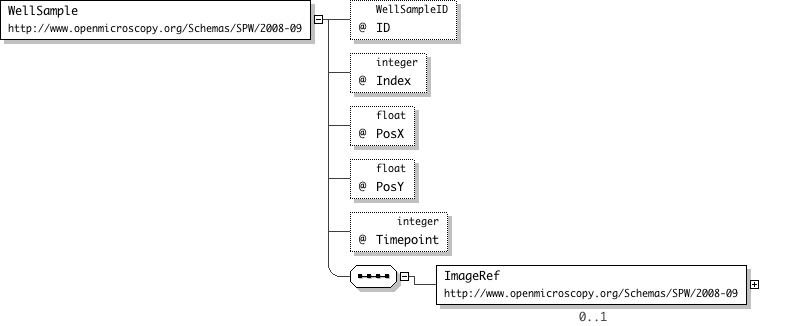
'This is redundant and will be removed'
"'The X position of the image within the well'
"'The Y position of the image within the well'
"'The time-point at which the image started to be collected'
">
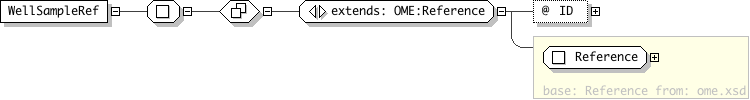
| Name | WellSampleRef |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element ScreenAcquisition |
| Type | Locally-defined complex type |
| Nillable | no |
| Abstract | no |
| Documentation | The WellSampleRef element is a reference to a WellSample element. |

| Super-types: | OME:LSID < PlateID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | PlateID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Plate , Element PlateRef |
| Content |
|

| Super-types: | OME:LSID < ReagentID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | ReagentID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Reagent , Element ReagentRef |
| Content |
|

| Super-types: | OME:LSID < ScreenAcquisitionID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | ScreenAcquisitionID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element ScreenAcquisition |
| Content |
|

| Super-types: | OME:LSID < ScreenID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | ScreenID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Screen , Element ScreenRef |
| Content |
|
| Super-types: | OME:LSID < WellID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | WellID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element Well |
| Content |
|
| Super-types: | OME:LSID < WellSampleID (by restriction) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: | None |
| Name | WellSampleID |
|---|---|
| Used by (from the same schema document) | Element WellSample , Element WellSampleRef |
| Content |
|
| Super-types: | Address < AusAddress (by extension) |
|---|---|
| Sub-types: |
|
| Name | AusAddress |
|---|---|
| Abstract | no |
The XML Instance Representation table above shows the schema component's content as an XML instance.
Abstract (Applies to complex type definitions and element declarations). An abstract element or complex type cannot used to validate an element instance. If there is a reference to an abstract element, only element declarations that can substitute the abstract element can be used to validate the instance. For references to abstract type definitions, only derived types can be used.
All Model Group Child elements can be provided in any order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-all.
Choice Model Group Only one from the list of child elements and model groups can be provided in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-choice.
Collapse Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32). Then, collapse contiguous sequences of space characters into single space character, and remove leading and trailing space characters.
Disallowed Substitutions
(Applies to element declarations). If substitution is specified, then substitution group members cannot be used in place of the given element declaration to validate element instances. If derivation methods, e.g. extension, restriction, are specified, then the given element declaration will not validate element instances that have types derived from the element declaration's type using the specified derivation methods. Normally, element instances can override their declaration's type by specifying an xsi:type attribute.
Key Constraint Like Uniqueness Constraint, but additionally requires that the specified value(s) must be provided. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Key Reference Constraint Ensures that the specified value(s) must match value(s) from a Key Constraint or Uniqueness Constraint. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.
Model Group Groups together element content, specifying the order in which the element content can occur and the number of times the group of element content may be repeated. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#Model_Groups.
Nillable
(Applies to element declarations). If an element declaration is nillable, instances can use the xsi:nil attribute. The xsi:nil attribute is the boolean attribute, nil, from the http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance namespace. If an element instance has an xsi:nil attribute set to true, it can be left empty, even though its element declaration may have required content.
Notation A notation is used to identify the format of a piece of data. Values of elements and attributes that are of type, NOTATION, must come from the names of declared notations. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cNotation_Declarations.
Preserve Whitespace Policy Preserve whitespaces exactly as they appear in instances.
Prohibited Derivations (Applies to type definitions). Derivation methods that cannot be used to create sub-types from a given type definition.
Prohibited Substitutions (Applies to complex type definitions). Prevents sub-types that have been derived using the specified derivation methods from validating element instances in place of the given type definition.
Replace Whitespace Policy Replace tab, line feed, and carriage return characters with space character (Unicode character 32).
Sequence Model Group Child elements and model groups must be provided in the specified order in instances. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#element-sequence.
Substitution Group Elements that are members of a substitution group can be used wherever the head element of the substitution group is referenced.
Substitution Group Exclusions (Applies to element declarations). Prohibits element declarations from nominating themselves as being able to substitute a given element declaration, if they have types that are derived from the original element's type using the specified derivation methods.
Target Namespace The target namespace identifies the namespace that components in this schema belongs to. If no target namespace is provided, then the schema components do not belong to any namespace.
Uniqueness Constraint Ensures uniqueness of an element/attribute value, or a combination of values, within a specified scope. See: http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1/#cIdentity-constraint_Definitions.